10 May 2024
Enabling Organisations’ Sustainability Transformation by Developing the Workforce Sustainability Competences
Mia Folkesson
Managing Partner
10 May 2024
Enabling Organisations’ Sustainability Transformation by Developing the Workforce Sustainability Competences
Mia Folkesson
Managing Partner
We are in the midst of a transformation. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Survey 2023 identified that 44% of surveyed companies are expecting the core skills of workers to change in the next five years (1). Furthermore, 60% of surveyed companies highlighted skills gaps in the local labour market as a barrier for businesses to transform.
At the same time, organisations increasingly recognise the value of proactively embracing sustainability initiatives (2). The push for sustainability is fuelled by regulatory pressure as well as stakeholder feedback (3). This pressure is universal to all companies no matter their size or sector (2). With this in mind, it should not come as a surprise that the broad application of ESG standards has been identified as one of the most influential macrotrends driving businesses to transform (1). There is a recognised need for professionals with the ability to effectively handle sustainability issues (4,5). Reports from the last few years show that the broader application of ESG standards has a positive impact on job creation as well as an increased demand for professionals with green skills (1,6).
These changes emphasise the requirement for continuous skills development in organisations.
Working life is changing because of these transformations and thus creates conditions for learning, which is why the workplace is seen as a key environment for continuous learning (7). At Impaktly, we recognise that the sustainability transformation requires thinking long-term. Each organisation’s journey is unique, ranging from those who have been working towards being sustainable for years and have been able to integrate it within their ways of being, to those just beginning to embed sustainability principles into their business strategies (8), as characterised in Figure 1.
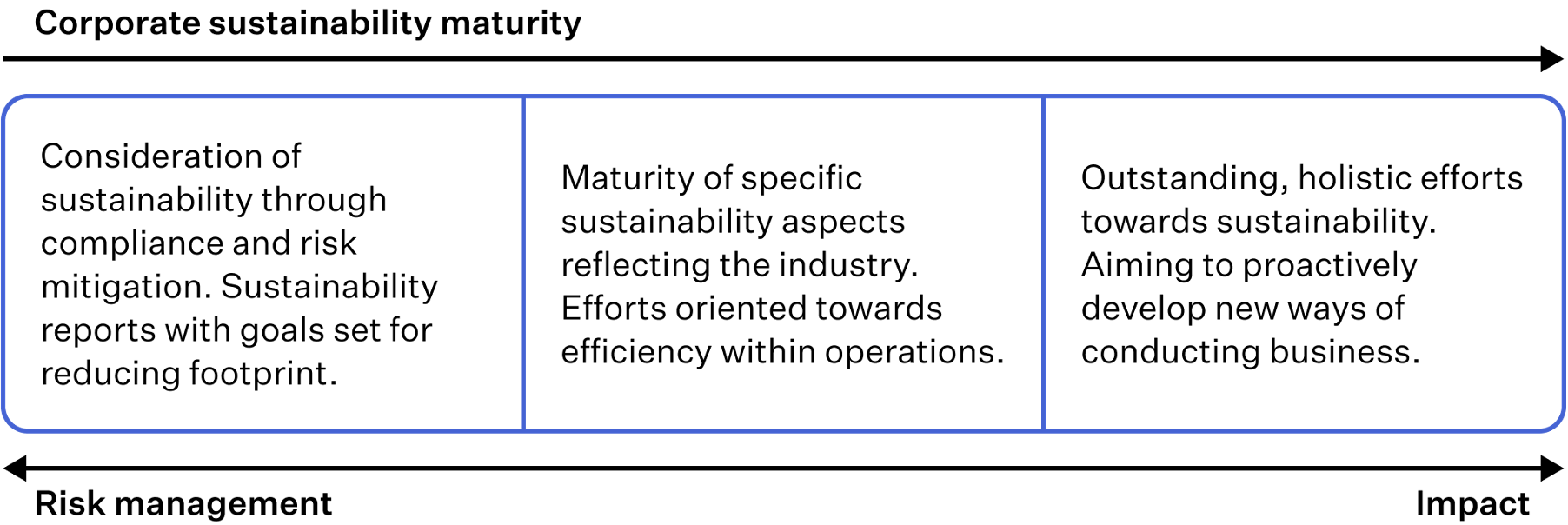
FIGURE 1: Three levels of corporate sustainability maturity.
At the current stage of the sustainability transformation, setting targets for carbon neutrality is gradually becoming commonplace due to regulation, and companies wishing to differentiate themselves from others must commit to sustainability actions that are harder to imitate (3).
To successfully adopt sustainability in the organisation’s practices and culture, the change must be organisation-wide and requires competences at all levels. This sustainability transformation requires employees and organisations to develop their competences to understand what sustainability is and more importantly how it affects them. Competence development helps organisations keep their talent and make sure their employees have the competences to do their jobs efficiently.
“The company grows if the employees grow, and the employees are the most important resource [...] they are the most important thing in the company.” (9)
As a result, an increasing number of organisations have recognised the importance of continuous learning and the need to upskill their existing employees to have adequate knowledge for the company to be able to reach their strategic goals (1,7). Sustainability competences are the knowledge and skills that enable successful task performance regarding real-world sustainability problems and opportunities (10).
Effective sustainability competence development is action-oriented, customised for each context and enables readiness to handle transformations.
While most learning in organisations is perceived to happen on the job from new projects and experiences, formal learning plays a crucial role in providing information to adopt into informal learning. We see that there are three key characteristics of effective sustainability competence development (9):
1. It emphasises actionable learning through practical experiences.
For sustainability competence development to be effective, it needs to emphasise actionable learning through practical experiences. Research on organisational learning advocates for practical learning tools and methods as well as learning through new experiences and social interactions instead of solely theory-focused learning (11).
Furthermore, sustainability competence development should prioritise tools and methods to facilitate learning by doing, to ensure learning extends beyond the formal sessions and becomes ingrained in daily work practices.
2. It fits the context of the organisation and specific function.
We understand that the sustainability competence development content needs to fit the context of the organisation. Because the material topic competences vary based on the industry and function, and organisations can be at diverse levels of sustainability maturity, it is imperative to tailor competence development accordingly. Material topic competences are the concrete sustainability knowledge needed due to one’s industry and function (12,13), examples of which are listed in Figure 2.

FIGURE 2: Material sustainability topic competences.
This requirement for customisation connects to the earlier characteristic of action-oriented training, as it underlines the need for sustainability competence development to be rooted in real-world scenarios that fit the context of the organisation. The choice of thematic content and how development happens needs to be carefully designed and deliberately coordinated with the intended learning outcomes (5).
3. It enables readiness to handle any transformation and find opportunities within them.
Finally, we believe that the most effective sustainability competence development integrates key sustainability competences which help organisations embed sustainability thinking into every aspect of organisational operations. Key sustainability competences are the skills applicable across various contexts, enabling individuals to handle transformations and find opportunities within them, as described in Figure 3 (10,14,15).

FIGURE 3: Key sustainability competences.
Here is how your organisation can take the next steps in developing the sustainability competences of your workforce:
1. Adopt Customised Learning Pathways. Improve the sustainability competences of your entire organisation through implementing customised learning programs that are tailored to fit different levels of the organisation. These learning pathways should consider the different realities of employees in different functions and incorporate real-world scenarios to ensure a practical understanding of sustainability.
2. Foster a Culture of Knowledge Sharing. Social learning is an effective way to learn in organisations. Thus, creating opportunities for employees at all levels to share insights and experiences related to sustainability can help in embedding sustainability across your organisation.
3. Commit to Ongoing Learning and Development. Recognise that developing sustainability competences is a continuous commitment, not just a one-time initiative. Regularly reassess and adapt your training programs to align with current sustainability challenges and evolving needs of your organisation. This proactive approach ensures that sustainability remains a core component of your organisation’s strategic goals.
Impaktly can help you develop the sustainability competences of your workforce to integrate sustainability into your way of being.
The key to effective implementation of sustainability competences lies in recognising the need for ongoing adjustments and a commitment to long-term development. Our sustainability competence development services are always characterised by practical learning that facilitates action that continues long after the formal training is concluded. The training is built based on individual organisation’s needs and wishes and caters to different organisational levels and their different realities.
We want to help build regenerative organisations capable of tackling future transformations head-on by ensuring organisations walk away with tangible tools and materials to use in their daily work. By enhancing the sustainability competences of organisations’ employees, they are equipped with the skills needed to navigate disruptions and transformations effectively.
About the author
This blog post is written by Iida Saaristomaa, a thesis worker at Impaktly, based on their master’s thesis on “Driving Sustainability Transformation Through Educating the Workforce – Productising Sustainability Competence Development” (9).
Let's talk about how to make this happen
We help you set the foundation and grow into becoming true business leaders in vast sustainability transformations.
Mia Folkesson
Managing Partner
mia@impaktly.com
Let's talk about how to make this happen
We help you set the foundation and grow into becoming true business leaders in vast sustainability transformations.
Mia Folkesson
Managing Partner
mia@impaktly.com